12 分,350+ 名
题目
T1. 文件夹操作日志搜集器
题目
每当用户执行变更文件夹操作时,LeetCode 文件系统都会保存一条日志记录。
下面给出对变更操作的说明:
"../":移动到当前文件夹的父文件夹。如果已经在主文件夹下,则 继续停留在当前文件夹 。"./":继续停留在当前文件夹。"x/":移动到名为x的子文件夹中。题目数据 保证总是存在文件夹x。
给你一个字符串列表 logs ,其中 logs[i] 是用户在 ith 步执行的操作。
文件系统启动时位于主文件夹,然后执行 logs 中的操作。
执行完所有变更文件夹操作后,请你找出 返回主文件夹所需的最小步数 。
示例 1:
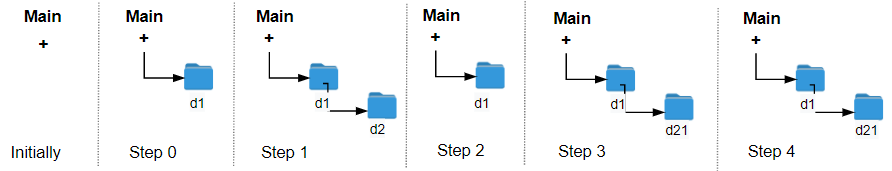
输入:logs = ["d1/","d2/","../","d21/","./"] 输出:2 解释:执行 "../" 操作变更文件夹 2 次,即可回到主文件夹
示例 2:
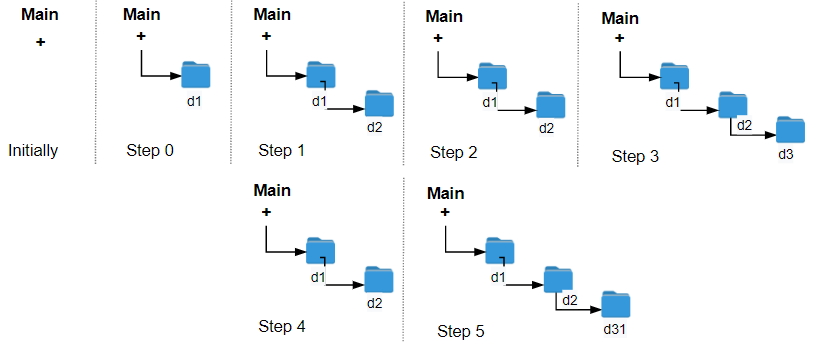
输入:logs = ["d1/","d2/","./","d3/","../","d31/"] 输出:3
示例 3:
输入:logs = ["d1/","../","../","../"] 输出:0
提示:
1 <= logs.length <= 1032 <= logs[i].length <= 10logs[i]包含小写英文字母,数字,'.'和'/'logs[i]符合语句中描述的格式- 文件夹名称由小写英文字母和数字组成
题解思路
- 模拟题
- 遇
"../"则res - 1 - 遇
"./"则不变 - 其他目录(不包括
"abc/def/")则res + 1
参考代码
public int minOperations(String[] logs) {
int res = 0;
for (String log : logs) {
if (log.equals("../")) res = Math.max(res - 1, 0);
else if (log.equals("./")) res = res;
else res++;
}
return res;
}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n) - 空间复杂度:
O(1)
T2. 经营摩天轮的最大利润
题目
你正在经营一座摩天轮,该摩天轮共有 4 个座舱 ,每个座舱 最多可以容纳 4 位游客 。你可以 逆时针 轮转座舱,但每次轮转都需要支付一定的运行成本 runningCost 。摩天轮每次轮转都恰好转动 1 / 4 周。
给你一个长度为 n 的数组 customers , customers[i] 是在第 i 次轮转(下标从 0 开始)之前到达的新游客的数量。这也意味着你必须在新游客到来前轮转 i 次。每位游客在登上离地面最近的座舱前都会支付登舱成本 boardingCost ,一旦该座舱再次抵达地面,他们就会离开座舱结束游玩。
你可以随时停下摩天轮,即便是 在服务所有游客之前 。如果你决定停止运营摩天轮,为了保证所有游客安全着陆,将免费进行所有后续轮转 。注意,如果有超过 4 位游客在等摩天轮,那么只有 4 位游客可以登上摩天轮,其余的需要等待 下一次轮转 。
返回最大化利润所需执行的 最小轮转次数 。 如果不存在利润为正的方案,则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
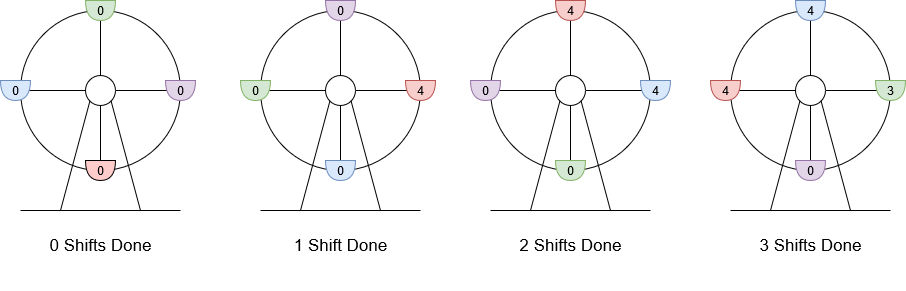
输入:customers = [8,3], boardingCost = 5, runningCost = 6 输出:3 解释:座舱上标注的数字是该座舱的当前游客数。 1. 8 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,4 位等待下一舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 4 * $5 - 1 * $6 = $14 。 2. 3 位游客抵达,4 位在等待的游客登舱,其他 3 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 8 * $5 - 2 * $6 = $28 。 3. 最后 3 位游客登舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 11 * $5 - 3 * $6 = $37 。 轮转 3 次得到最大利润,最大利润为 $37 。
示例 2:
输入:customers = [10,9,6], boardingCost = 6, runningCost = 4 输出:7 解释: 1. 10 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,6 位等待下一舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 4 * $6 - 1 * $4 = $20 。 2. 9 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,11 位等待(2 位是先前就在等待的,9 位新加入等待的),摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 8 * $6 - 2 * $4 = $40 。 3. 最后 6 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,13 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 12 * $6 - 3 * $4 = $60 。 4. 4 位登舱,9 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 16 * $6 - 4 * $4 = $80 。 5. 4 位登舱,5 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 20 * $6 - 5 * $4 = $100 。 6. 4 位登舱,1 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 24 * $6 - 6 * $4 = $120 。 7. 1 位登舱,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 25 * $6 - 7 * $4 = $122 。 轮转 7 次得到最大利润,最大利润为$122 。
示例 3:
输入:customers = [3,4,0,5,1], boardingCost = 1, runningCost = 92 输出:-1 解释: 1. 3 位游客抵达,3 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 3 * $1 - 1 * $92 = -$89 。 2. 4 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 is 7 * $1 - 2 * $92 = -$177 。 3. 0 位游客抵达,0 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 7 * $1 - 3 * $92 = -$269 。 4. 5 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,1 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 12 * $1 - 4 * $92 = -$356 。 5. 1 位游客抵达,2 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 13 * $1 - 5 * $92 = -$447 。 利润永不为正,所以返回 -1 。
示例 4:
输入:customers = [10,10,6,4,7], boardingCost = 3, runningCost = 8 输出:9 解释: 1. 10 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,6 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 4 * $3 - 1 * $8 = $4 。 2. 10 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,12 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 8 * $3 - 2 * $8 = $8 。 3. 6 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,14 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 12 * $3 - 3 * $8 = $12 。 4. 4 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,14 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 16 * $3 - 4 * $8 = $16 。 5. 7 位游客抵达,4 位登舱,17 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 20 * $3 - 5 * $8 = $20 。 6. 4 位登舱,13 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 24 * $3 - 6 * $8 = $24 。 7. 4 位登舱,9 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 28 * $3 - 7 * $8 = $28 。 8. 4 位登舱,5 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 32 * $3 - 8 * $8 = $32 。 9. 4 位登舱,1 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 36 * $3 - 9 * $8 = $36 。 10. 1 位登舱,0 位等待,摩天轮轮转。当前利润为 37 * $3 - 10 * $8 = $31 。 轮转 9 次得到最大利润,最大利润为 $36 。
提示:
n == customers.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= customers[i] <= 501 <= boardingCost, runningCost <= 100
题解思路
- 模拟题
- 遍历游客,累计利润
total - 记录轮次
i,最后返回res
参考代码
public int minOperationsMaxProfit(int[] arr, int b, int r) {
int max = 0, total = 0; // 利润
int i = 0, res = 0; // 次数
int curr = 0; // 等待人数
for (int cnt : arr) {
curr += cnt;
int board = Math.min(4, curr);
curr -= board;
total += board * b - r;
i++;
if (total > max) {
max = total;
res = i;
}
}
while (curr > 0) {
int board = Math.min(4, curr);
curr -= board;
total += board * b - r;
i++;
if (total > max) {
max = total;
res = i;
}
}
return max == 0 ? -1 : res;
}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n) - 空间复杂度:
O(1)
T3. 皇位继承顺序
题目
一个王国里住着国王、他的孩子们、他的孙子们等等。每一个时间点,这个家庭里有人出生也有人死亡。
这个王国有一个明确规定的皇位继承顺序,第一继承人总是国王自己。我们定义递归函数 Successor(x, curOrder) ,给定一个人 x 和当前的继承顺序,该函数返回 x 的下一继承人。
Successor(x, curOrder):
如果 x 没有孩子或者所有 x 的孩子都在 curOrder 中:
如果 x 是国王,那么返回 null
否则,返回 Successor(x 的父亲, curOrder)
否则,返回 x 不在 curOrder 中最年长的孩子
比方说,假设王国由国王,他的孩子 Alice 和 Bob (Alice 比 Bob 年长)和 Alice 的孩子 Jack 组成。
- 一开始,
curOrder为["king"]. - 调用
Successor(king, curOrder),返回 Alice ,所以我们将 Alice 放入curOrder中,得到["king", "Alice"]。 - 调用
Successor(Alice, curOrder),返回 Jack ,所以我们将 Jack 放入curOrder中,得到["king", "Alice", "Jack"]。 - 调用
Successor(Jack, curOrder),返回 Bob ,所以我们将 Bob 放入curOrder中,得到["king", "Alice", "Jack", "Bob"]。 - 调用
Successor(Bob, curOrder),返回null。最终得到继承顺序为["king", "Alice", "Jack", "Bob"]。
通过以上的函数,我们总是能得到一个唯一的继承顺序。
请你实现 ThroneInheritance 类:
ThroneInheritance(string kingName)初始化一个ThroneInheritance类的对象。国王的名字作为构造函数的参数传入。void birth(string parentName, string childName)表示parentName新拥有了一个名为childName的孩子。void death(string name)表示名为name的人死亡。一个人的死亡不会影响Successor函数,也不会影响当前的继承顺序。你可以只将这个人标记为死亡状态。string[] getInheritanceOrder()返回 除去 死亡人员的当前继承顺序列表。
示例:
输入:
["ThroneInheritance", "birth", "birth", "birth", "birth", "birth", "birth", "getInheritanceOrder", "death", "getInheritanceOrder"]
[["king"], ["king", "andy"], ["king", "bob"], ["king", "catherine"], ["andy", "matthew"], ["bob", "alex"], ["bob", "asha"], [null], ["bob"], [null]]
输出:
[null, null, null, null, null, null, null, ["king", "andy", "matthew", "bob", "alex", "asha", "catherine"], null, ["king", "andy", "matthew", "alex", "asha", "catherine"]]
解释:
ThroneInheritance t= new ThroneInheritance("king"); // 继承顺序:king
t.birth("king", "andy"); // 继承顺序:king > andy
t.birth("king", "bob"); // 继承顺序:king > andy > bob
t.birth("king", "catherine"); // 继承顺序:king > andy > bob > catherine
t.birth("andy", "matthew"); // 继承顺序:king > andy > matthew > bob > catherine
t.birth("bob", "alex"); // 继承顺序:king > andy > matthew > bob > alex > catherine
t.birth("bob", "asha"); // 继承顺序:king > andy > matthew > bob > alex > asha > catherine
t.getInheritanceOrder(); // 返回 ["king", "andy", "matthew", "bob", "alex", "asha", "catherine"]
t.death("bob"); // 继承顺序:king > andy > matthew > bob(已经去世)> alex > asha > catherine
t.getInheritanceOrder(); // 返回 ["king", "andy", "matthew", "alex", "asha", "catherine"]
提示:
1 <= kingName.length, parentName.length, childName.length, name.length <= 15kingName,parentName,childName和name仅包含小写英文字母。- 所有的参数
childName和kingName互不相同。 - 所有
death函数中的死亡名字name要么是国王,要么是已经出生了的人员名字。 - 每次调用
birth(parentName, childName)时,测试用例都保证parentName对应的人员是活着的。 - 最多调用
105次birth和death。 - 最多调用
10次getInheritanceOrder。
题解思路
- 题目一堆,就是前序遍历(每次都遍历也是暴力了…)
- 建模,构造
Node树
参考代码
// 构造节点
class Node {
String name;
List<Node> children;
boolean alive;
Node(String name) {
this.name = name;
children = new LinkedList<>();
alive = true;
}
void death() {
alive = false;
}
}
private List<String> list;
private Node root;
private Map<String, Node> map;
private boolean oper; // 是否有变更过
public ThroneInheritance(String kingName) {
root = new Node(kingName);
map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(kingName, root);
oper = true;
}
public void birth(String parentName, String childName) {
Node parent = map.get(parentName);
Node child = new Node(childName);
map.put(childName, child);
parent.children.add(child);
oper = true;
}
public void death(String name) {
Node person = map.get(name);
person.death();
oper = true;
}
public List<String> getInheritanceOrder() {
if (!oper) return list;
oper = false;
list = new LinkedList<>();
dfs(root);
return list;
}
// dfs: pre-order
private void dfs(Node node) {
if (node == null) return;
if (node.alive) list.add(node.name);
for (Node child : node.children) {
dfs(child);
}
}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
- 生/死:
O(1) - 查:
O(n)
- 生/死:
- 空间复杂度:
O(n)
T4. 最多可达成的换楼请求数目
题目
我们有 n 栋楼,编号从 0 到 n - 1 。每栋楼有若干员工。由于现在是换楼的季节,部分员工想要换一栋楼居住。
给你一个数组 requests ,其中 requests[i] = [fromi, toi] ,表示一个员工请求从编号为 fromi 的楼搬到编号为 toi 的楼。
一开始 所有楼都是满的,所以从请求列表中选出的若干个请求是可行的需要满足 每栋楼员工净变化为 0 。意思是每栋楼 离开 的员工数目 等于 该楼 搬入 的员工数数目。比方说 n = 3 且两个员工要离开楼 0 ,一个员工要离开楼 1 ,一个员工要离开楼 2 ,如果该请求列表可行,应该要有两个员工搬入楼 0 ,一个员工搬入楼 1 ,一个员工搬入楼 2 。
请你从原请求列表中选出若干个请求,使得它们是一个可行的请求列表,并返回所有可行列表中最大请求数目。
示例 1:
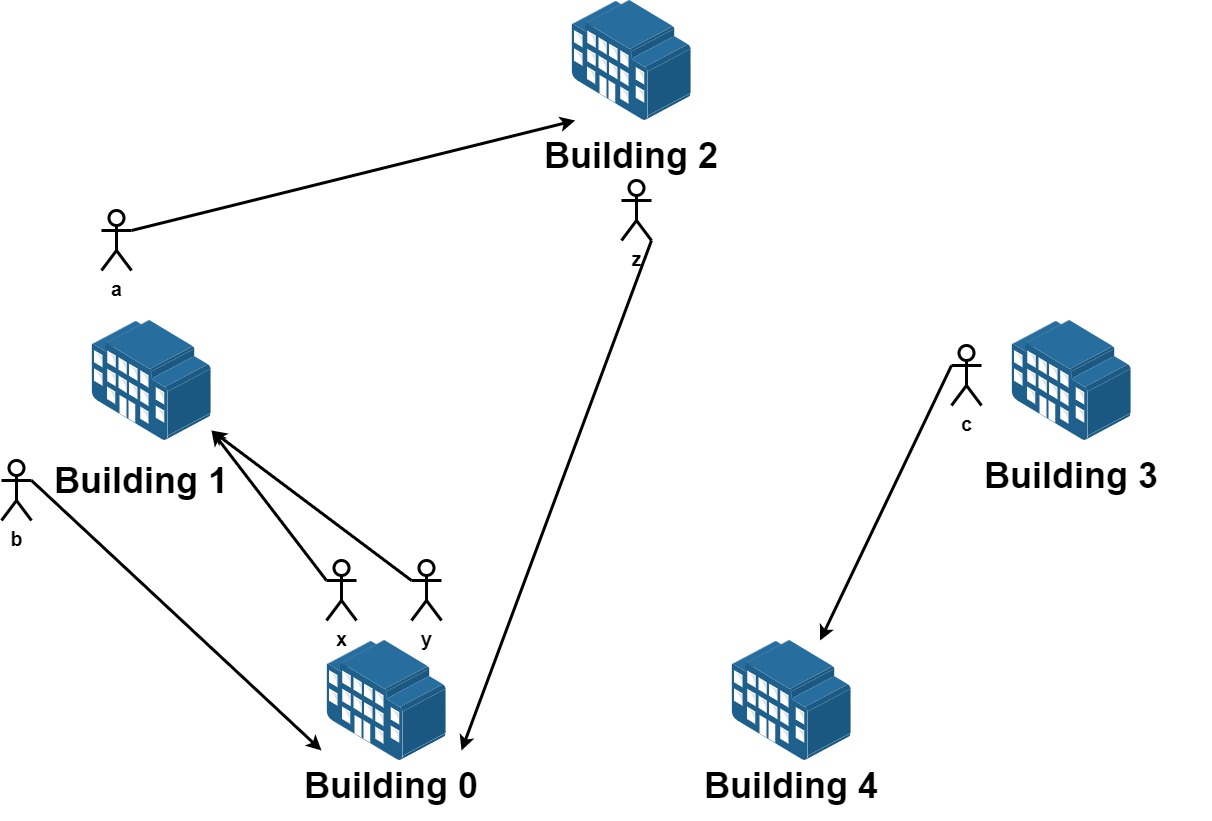
输入:n = 5, requests = [[0,1],[1,0],[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[3,4]] 输出:5 解释:请求列表如下: 从楼 0 离开的员工为 x 和 y ,且他们都想要搬到楼 1 。 从楼 1 离开的员工为 a 和 b ,且他们分别想要搬到楼 2 和 0 。 从楼 2 离开的员工为 z ,且他想要搬到楼 0 。 从楼 3 离开的员工为 c ,且他想要搬到楼 4 。 没有员工从楼 4 离开。 我们可以让 x 和 b 交换他们的楼,以满足他们的请求。 我们可以让 y,a 和 z 三人在三栋楼间交换位置,满足他们的要求。 所以最多可以满足 5 个请求。
示例 2:
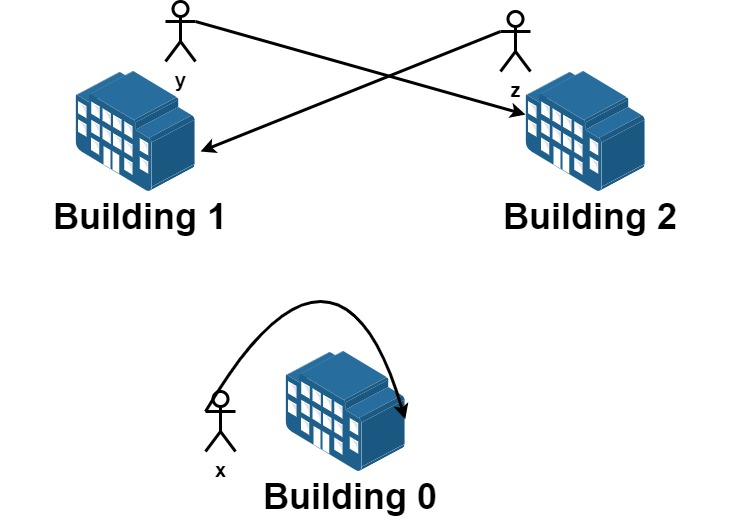
输入:n = 3, requests = [[0,0],[1,2],[2,1]] 输出:3 解释:请求列表如下: 从楼 0 离开的员工为 x ,且他想要回到原来的楼 0 。 从楼 1 离开的员工为 y ,且他想要搬到楼 2 。 从楼 2 离开的员工为 z ,且他想要搬到楼 1 。 我们可以满足所有的请求。
示例 3:
输入:n = 4, requests = [[0,3],[3,1],[1,2],[2,0]] 输出:4
提示:
1 <= n <= 201 <= requests.length <= 16requests[i].length == 20 <= fromi, toi < n
题解思路
- 数据范围不大,回溯硬刚
- 记录每栋楼出入度合计,要求最后都为
0 - 对请求
req[i]要么满足,要么不满足
参考代码
public int maximumRequests(int n, int[][] requests) {
return bt(requests, 0, 0, new int[n]);
}
private int bt(int[][] req, int i, int cnt, int[] degree) {
if (i == req.length) {
for (int d : degree)
if (d != 0) return 0;
return cnt;
}
int from = req[i][0], to = req[i][1];
// 满足 req[i]
degree[from]--; degree[to]++;
int notSkip = bt(req, i + 1, cnt + 1, degree);
degree[from]++; degree[to]--;
// 不满足 req[i]
int skip = bt(req, i + 1, cnt, degree);
return Math.max(notSkip, skip);
}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(2^len)T(len) = 2T(len - 1) + O(1)
- 空间复杂度:
O(n)